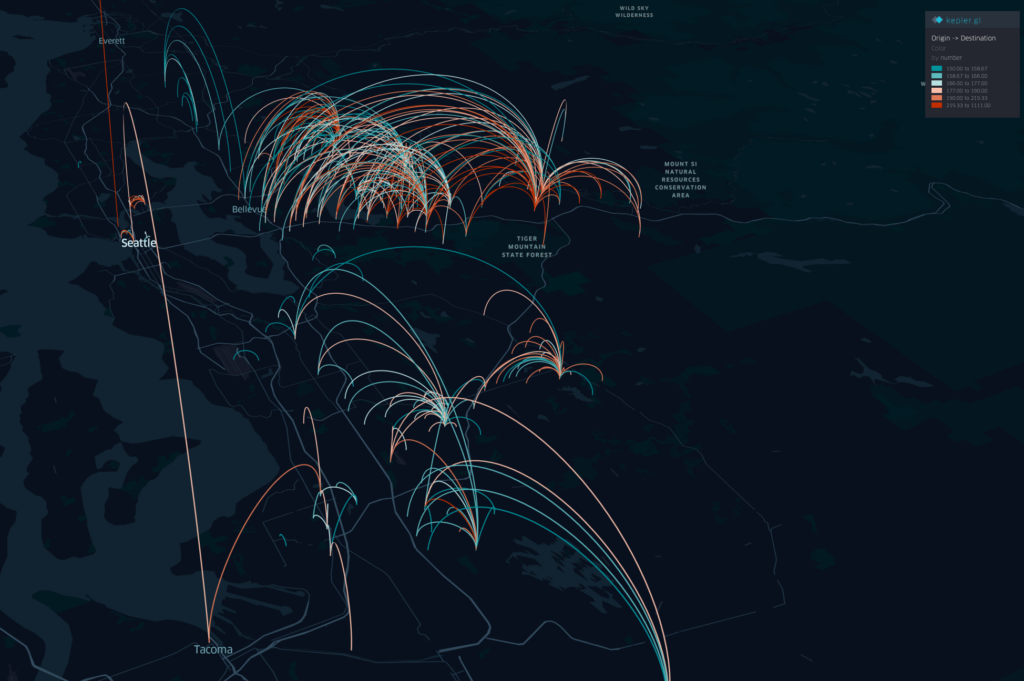
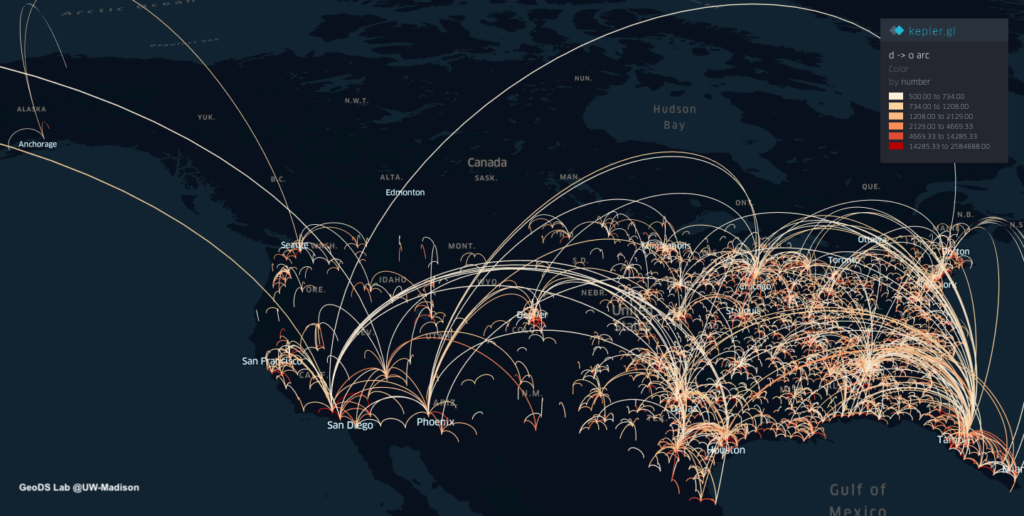
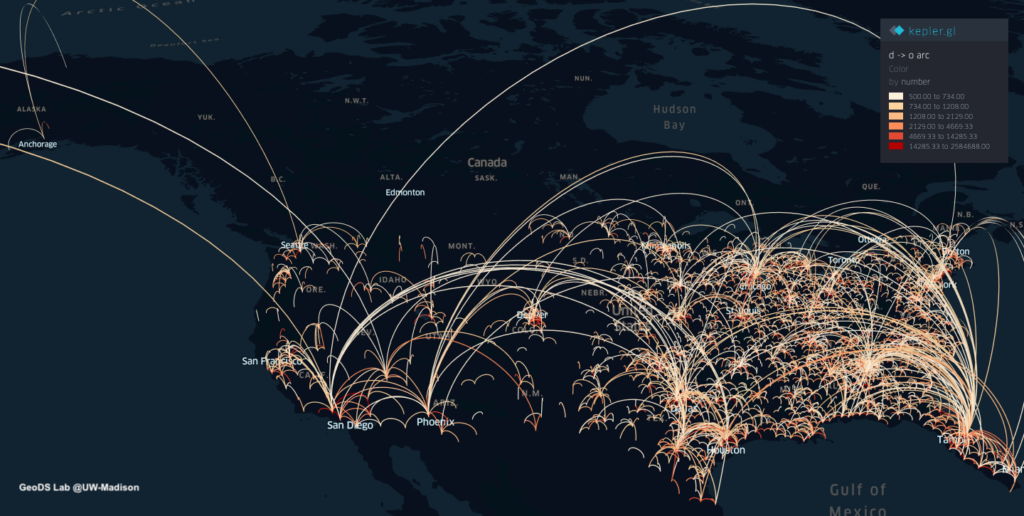
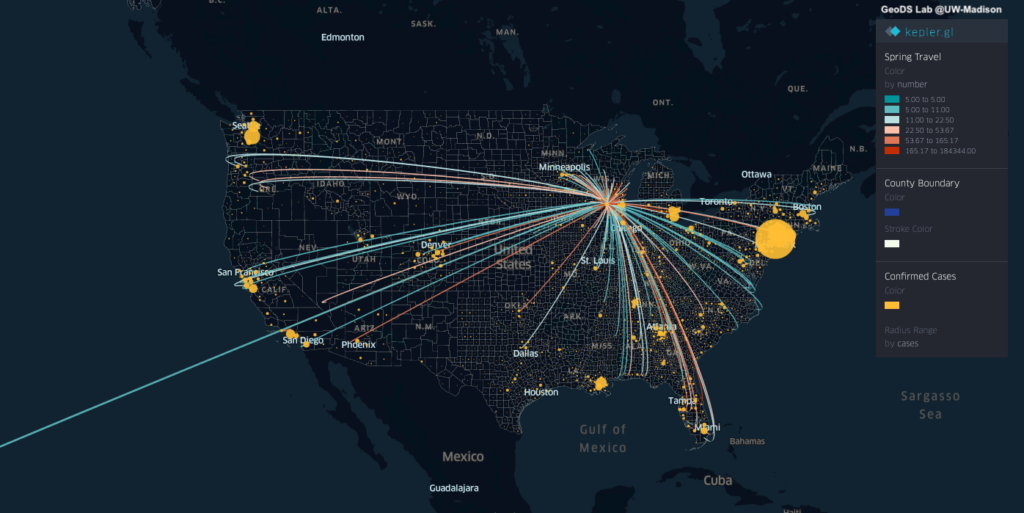
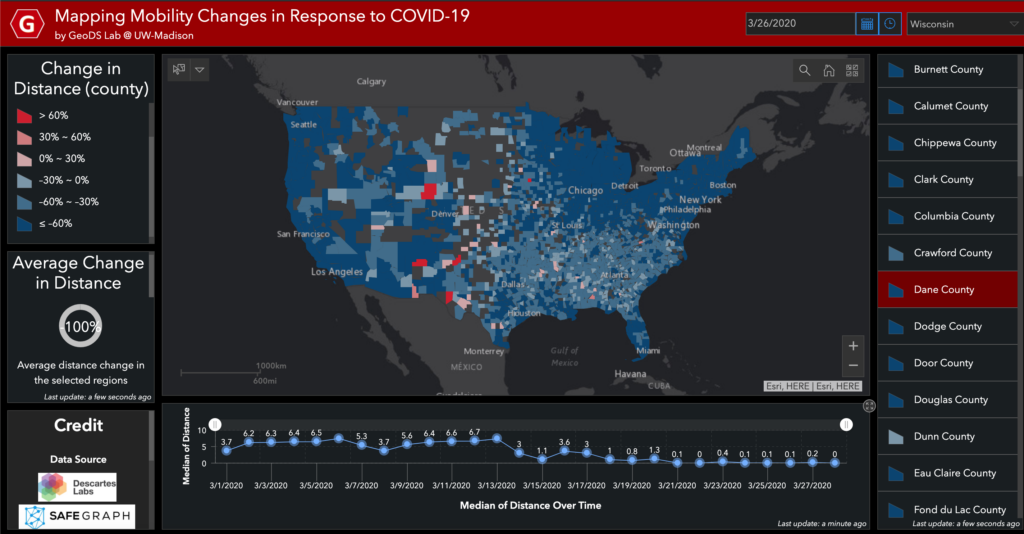
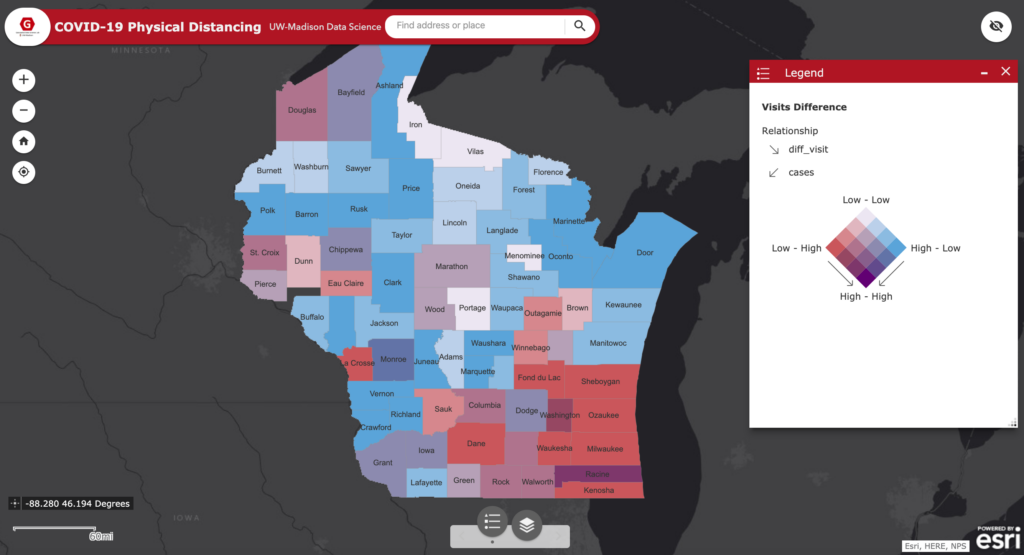
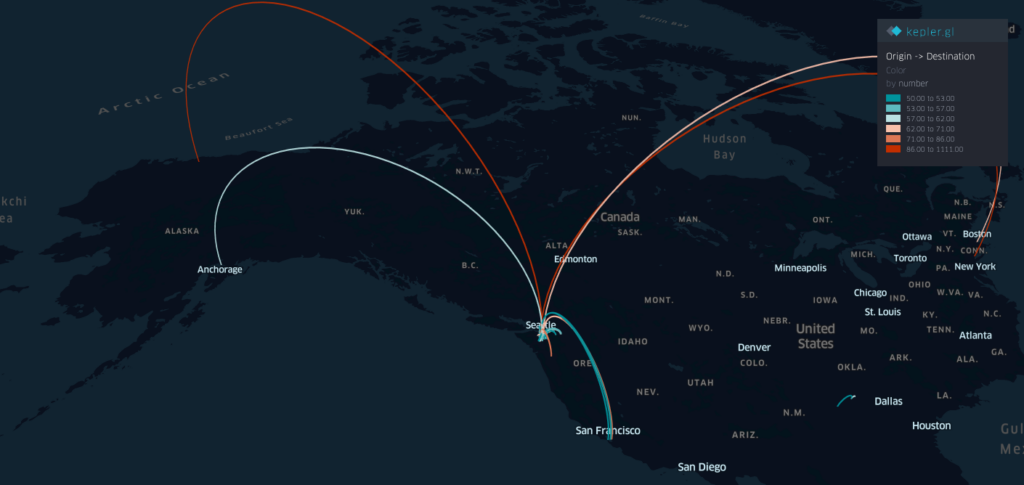
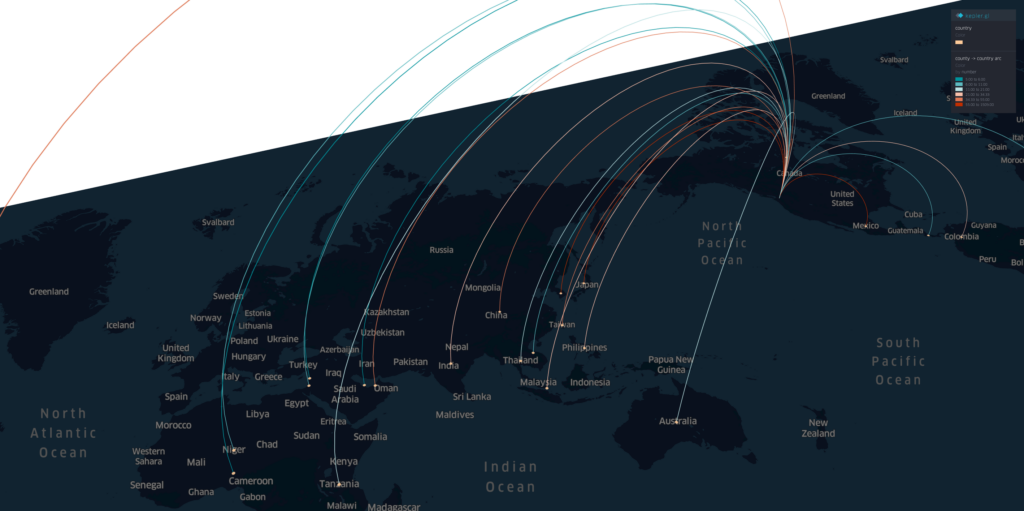
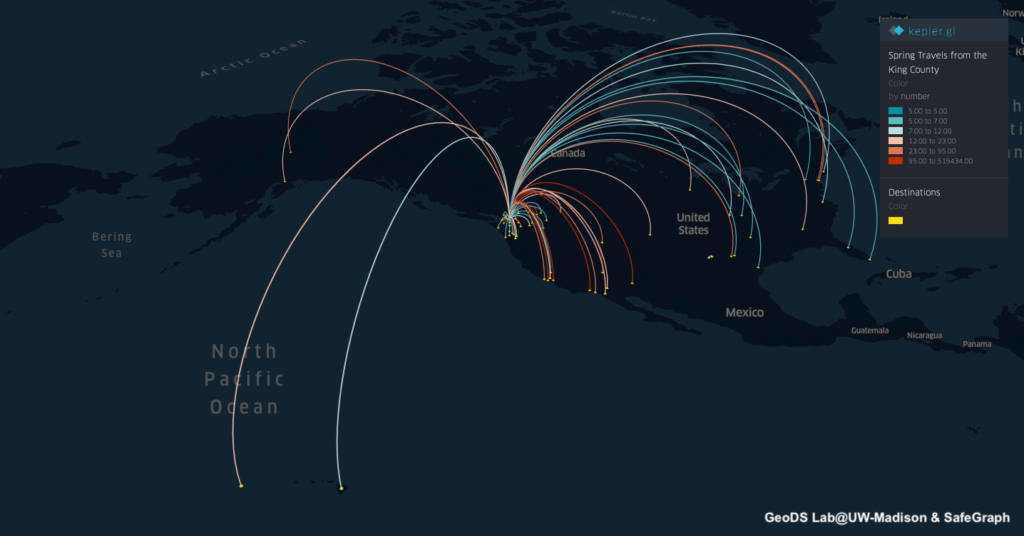
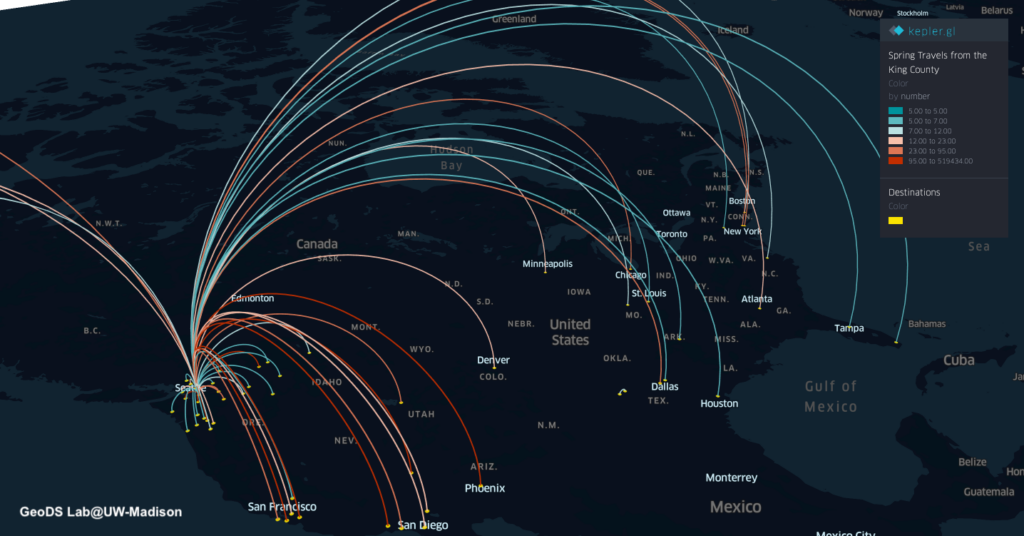
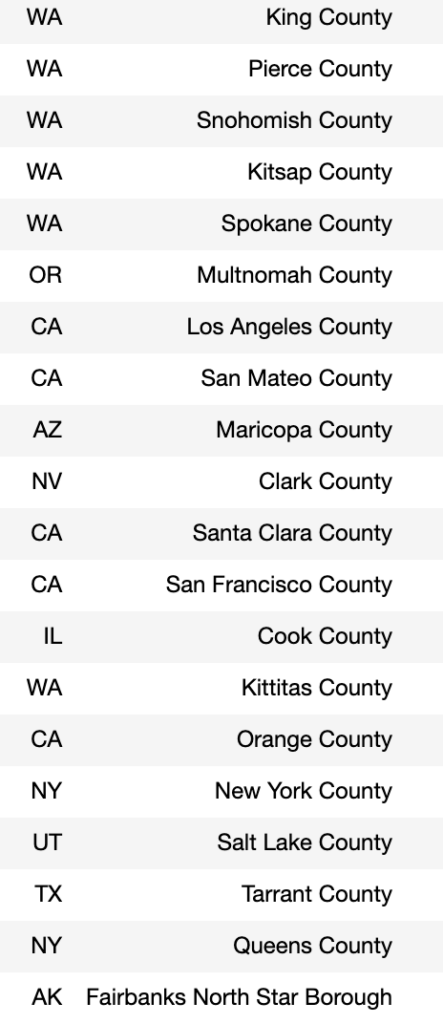
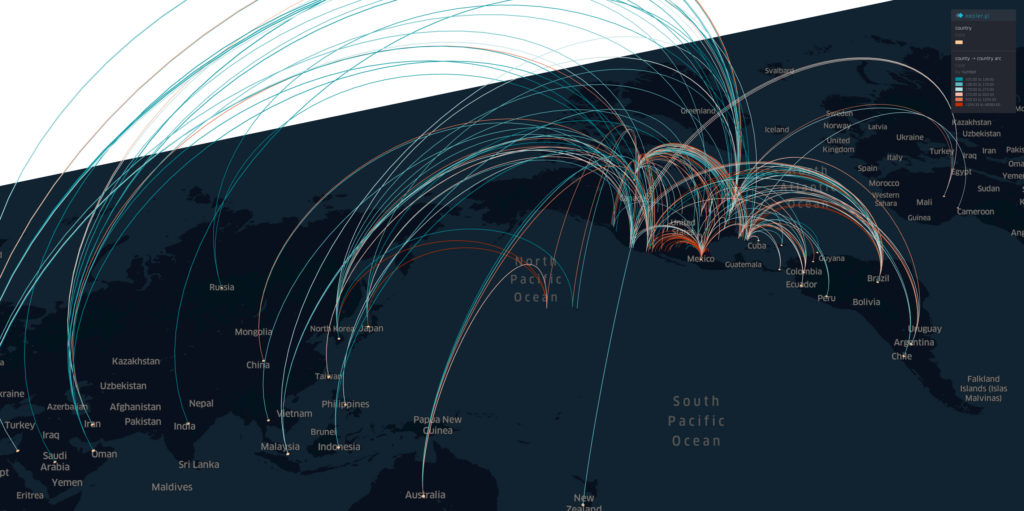
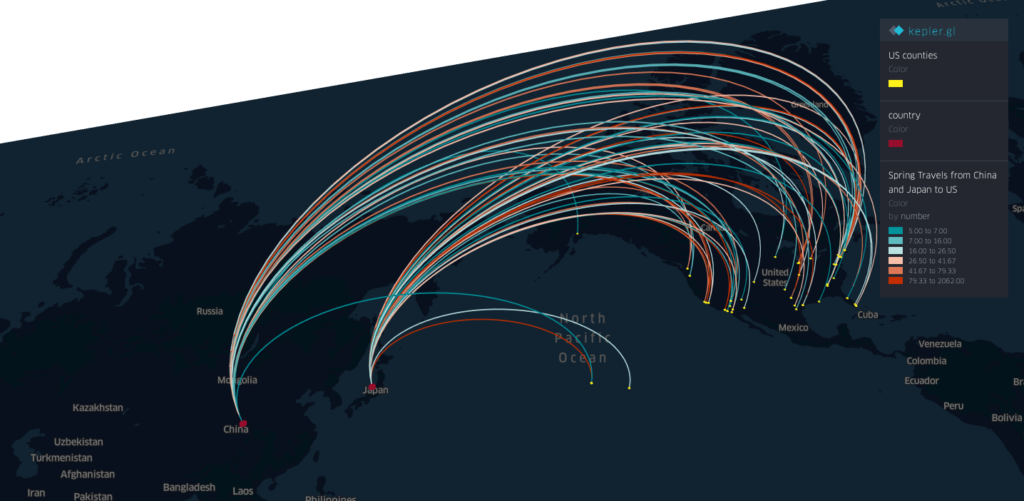
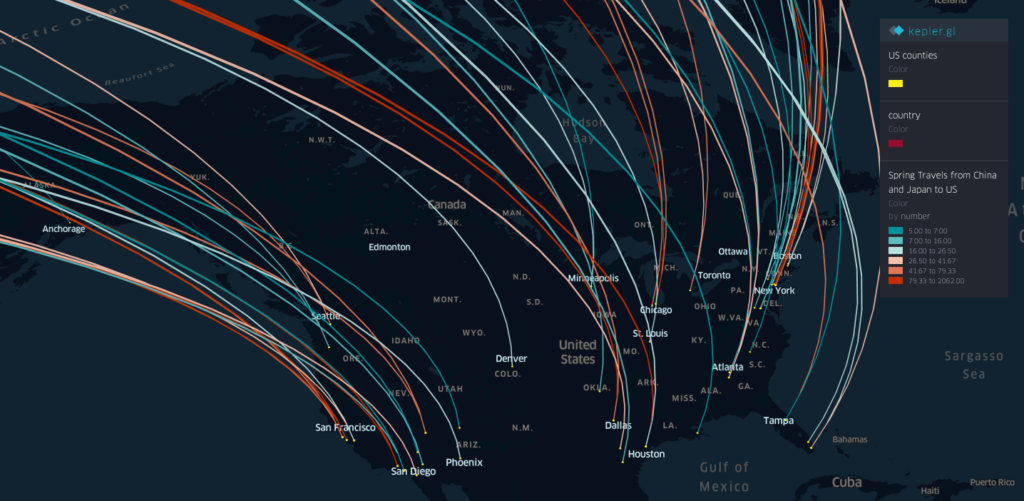
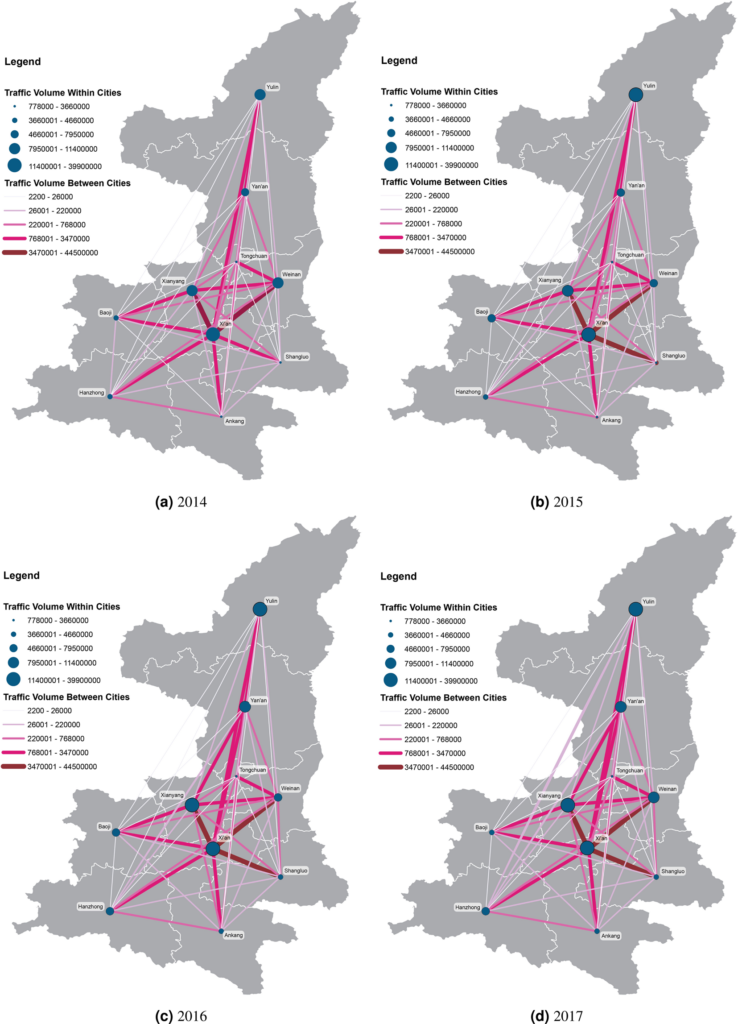
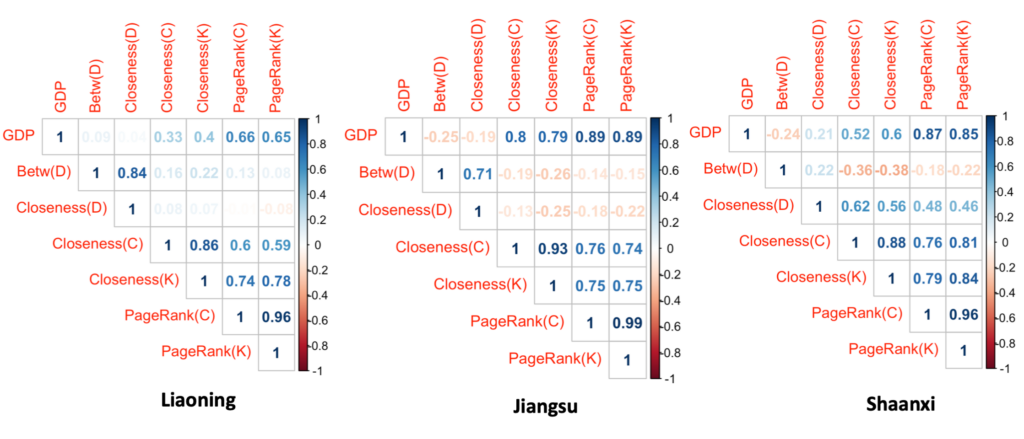
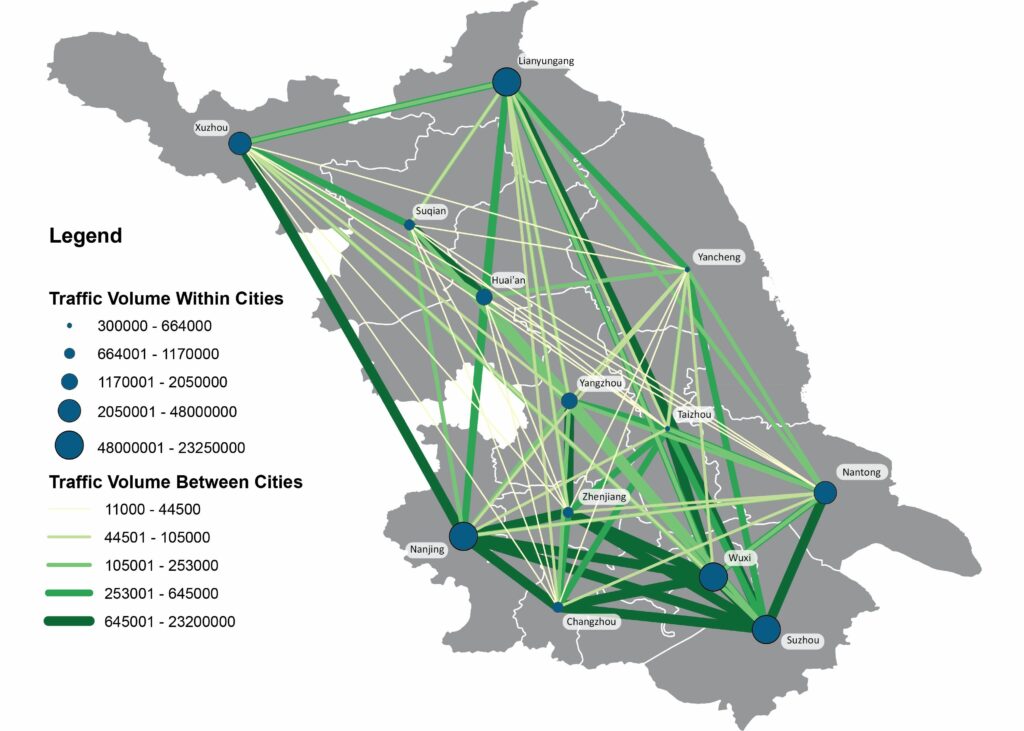
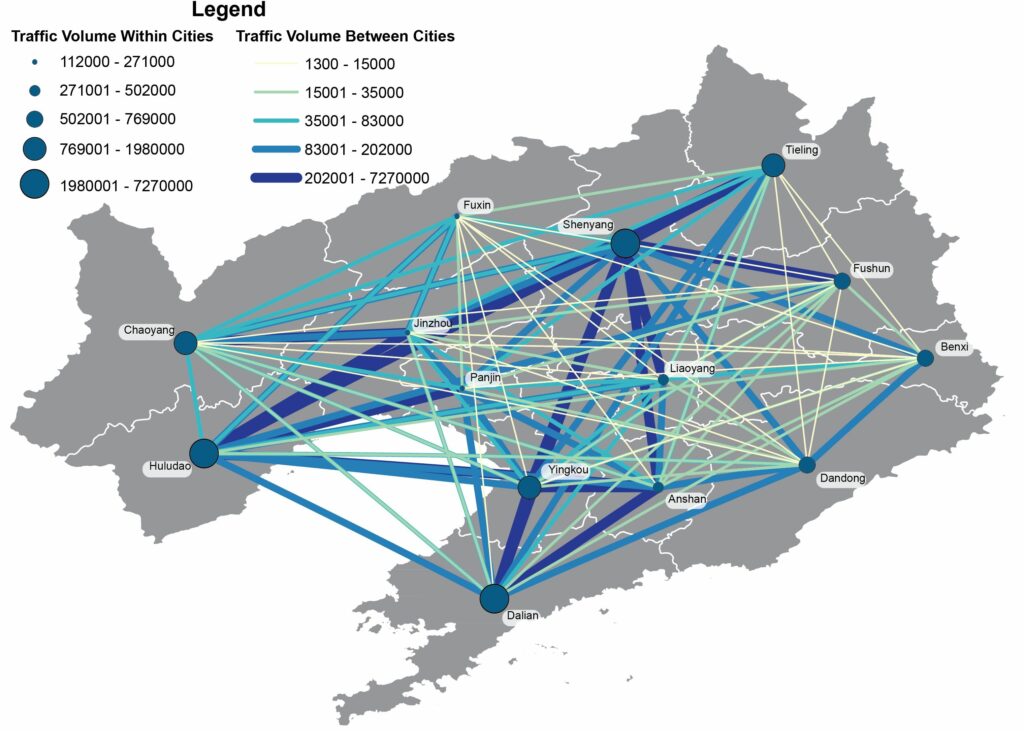
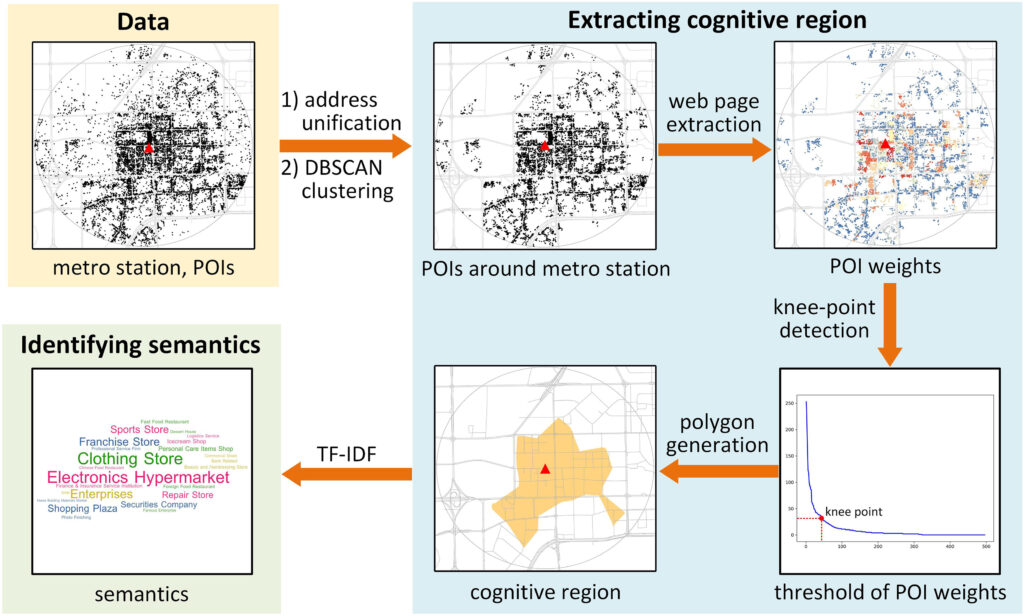
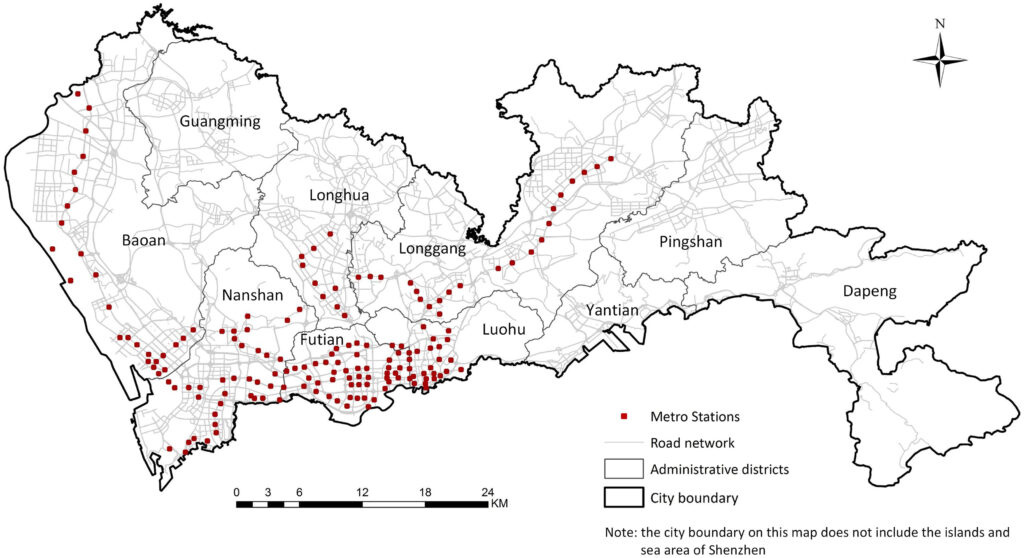
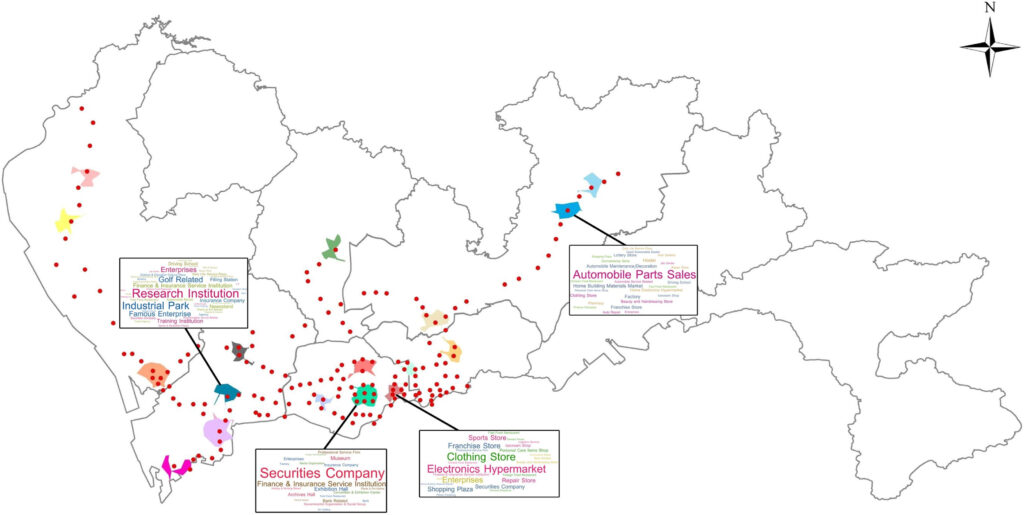
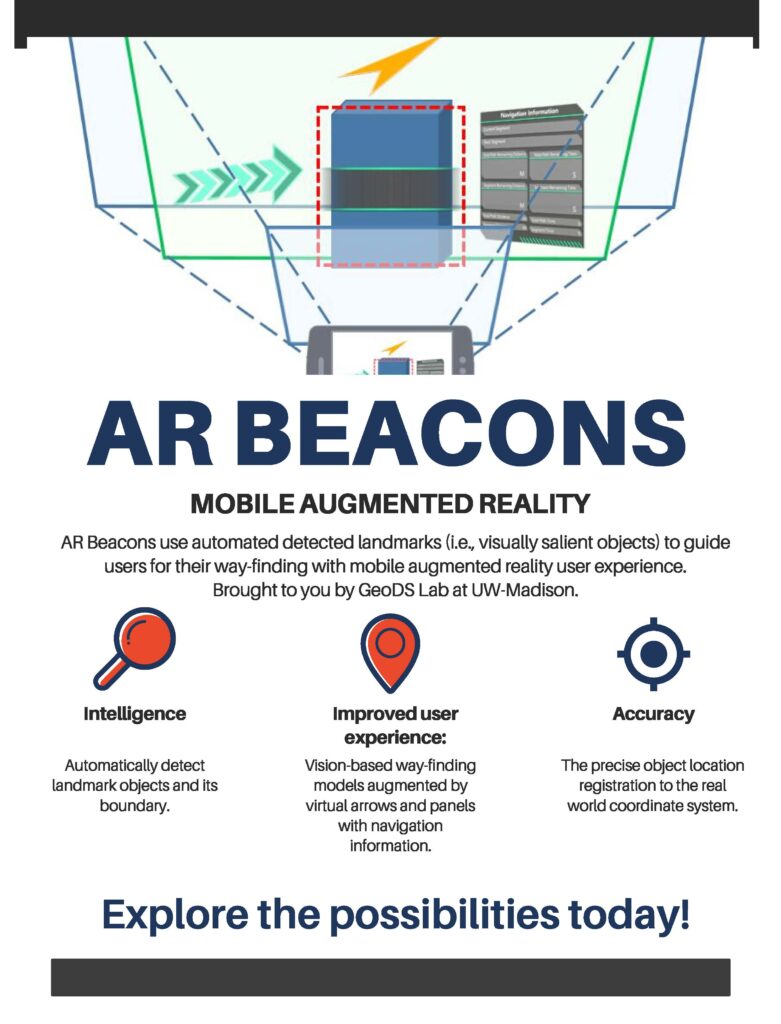
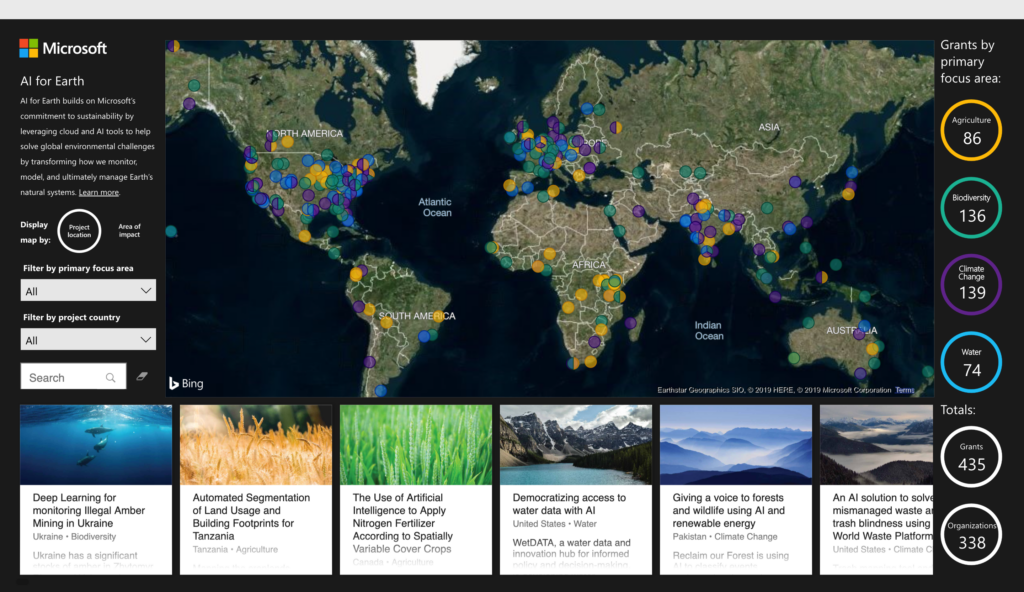
Projects address human mobility patterns, access to health care and food systems, racial and disability disparities during the pandemic.
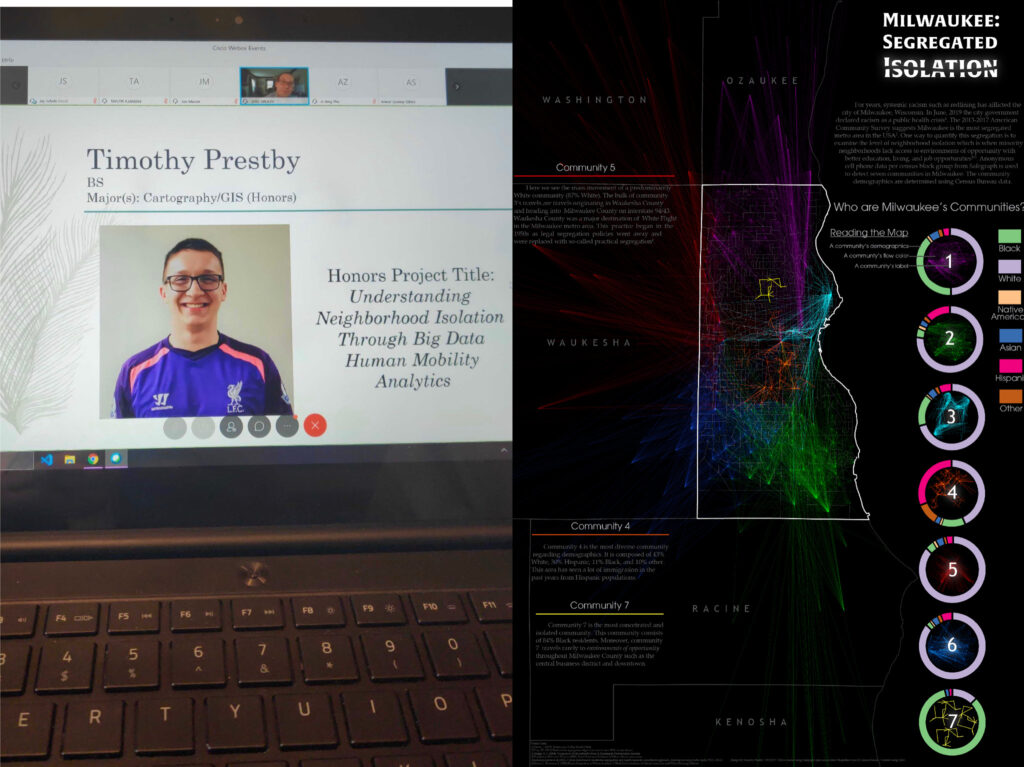
The Geospatial Software Institute (GSI) Conceptualization Project has announced 16 fellowships to researchers at 13 institutions to tackle COVID-19 challenges using geospatial software and advanced capabilities in cyberinfrastructure and data science. Prof. Song Gao was selected as one of the geospatial fellows. A full list of the fellows, with biographies and project information, is at https://gsi.cigi.illinois.edu/geospatial-fellows-members/.
The GSI Conceptualization Project is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), and carried out in partnership with the American Association of Geographers (AAG), Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc. (CUAHSI), the National Opinion Research Center (NORC) at the University of Chicago, Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), and University Consortium for Geographic Information Science (UCGIS). Technical and cyberinfrastructure support are provided by the CyberGIS Center for Advanced Digital and Spatial Studies (CyberGIS Center) at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
“The COVID-19 crisis has shown how critical it is to have cutting-edge geospatial software and cyberinfrastructure to tackle the pandemic’s many challenges,” said Shaowen Wang, the principal investigator of the NSF project and founding director of the CyberGIS Center. “We are extremely grateful for NSF’s support to fund this talented group of researchers, whose work is so diverse yet complementary.”
Michael Goodchild, chair of the NSF project advisory committee and professor emeritus in geography at UC-Santa Barbara, agreed. “Geospatial data and tools have enormous potential for helping us address the challenges of COVID-19, and these 16 Fellows have exactly the right qualifications and experience. I’m very excited to see what they are able to achieve.”
The Fellows come from varied professional, cultural, and institutional backgrounds, representing many disciplinary areas, including public health, food access, emergency management, housing and neighborhood change, and community-based mapping. The fellowship projects represent frontiers of emerging geospatial data science, including for example geospatial AI and deep learning, geovisualization, and advanced approaches to gathering and analyzing geospatial data.
Pioneered by multi-million dollar research funded by NSF, cyberGIS (i.e., cyber geographic information science and systems based on advanced computing and cyberinfrastructure) has emerged as a new generation of GIS, comprising a seamless integration of advanced cyberinfrastructure, GIS, and spatial analysis and modeling capabilities while leading to widespread research advances and broad societal impacts. Built on the progress made by cyberGIS-related communities, the GSI conceptualization project is charged with developing a strategic plan for a long-term hub of excellence in geospatial software infrastructure, one that can better address emergent issues of food security, ecology, emergency management, environmental research and stewardship, national security, public health, and more.
The Geospatial Fellows program will enable diverse researchers and educators to harness geospatial software and data at scale, in reproducible and transparent ways; and will contribute to the nation’s workforce capability and capacity to utilize geospatial big data and software for knowledge discovery. With a particular focus on COVID-19, the combined research findings of the Fellows will offer insight on how to make geospatial research computationally reproducible and transparent, while also developing novel methods, including analysis, simulation, and modeling, to study the spread and impacts of the virus. The Fellows’ research will substantially add to public understanding of the societal impacts of COVID-19 on different communities, assessing the social and spatial disparities of COVID-19 among vulnerable populations.
“I look forward to seeing the results of these projects, particularly as FAIR and open datasets, software, and models that others can then build on,” says Daniel S. Katz, Assistant Director for Scientific Software and Applications at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA), the University of Illinois.
For more information about the GSI conceptualization project, see their website: https://gsi.cigi.illinois.edu/.
For a list of Geospatial Fellows and their projects, visit https://gsi.cigi.illinois.edu/geospatial-fellows-members/.